ASP.NET Core Blazor | DataGrid Paging
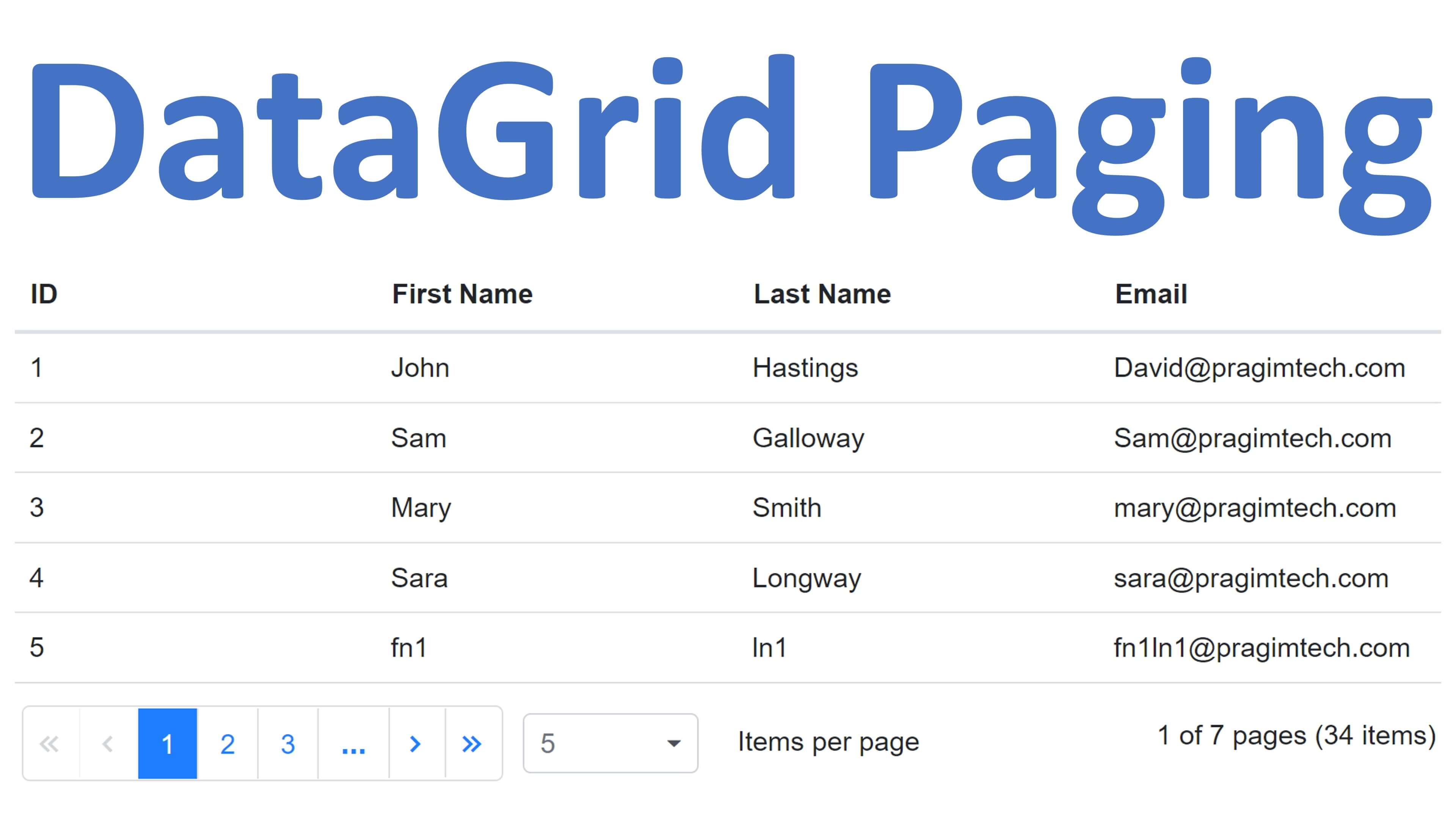
In this video we will discuss how to perform Paging in Blazor DataGrid. The support for Paging is provided out of the box by Syncfusion DataGrid component. It's very powerful and offers several features like
- Adaptive UI
- Touch Support
- Globalization and Localization
- Export to Excel, PDF and CSV
- Sorting, Paging, Filtering, Grouping
- Supports all the CRUD operations
- Aggregated Column Values and
- many more
You will be amazed by the power and functionality the DataGrid component bring to your Blazor app. Saves a lot of development time and effort. It is very easy to integrate, configure and use.
Syncfusion Components
Syncfusion components are free if you are an individual or a company and meet the following 2 conditions.
- Less than $1 million USD in annual gross revenue and
- 5 or fewer developers
Use the following link to claim the free community license
https://www.syncfusion.com/products/communitylicense
Add Syncfusion DataGrid component to Blazor application
We discussed how to add and configure Syncfusion DataGrid component in Part 4 of Web Development with Blazor video series. Click here for the course page where you will find all the videos and text articles in sequence.
Step 1 : Install "Syncfusion.Blazor.Grid" nuget package
Step 2 : For styling, reference Syncfusion Bootstrap theme file in index.html file. In a Blazor WebAssembly project, you will find index.html file in "wwwroot" folder.
Step 3 : In "imports.razor" file, include the following 2 using declarations
@using Syncfusion.Blazor
@using Syncfusion.Blazor.GridsStep 4 : Register Syncfusion Blazor services. We do this in the Main() method in "Program.cs" file.
builder.services.AddSyncfusionBlazor()At this point you can use Syncfusion DataGrid component on any of your Blazor application pages.
@if (Employees != null)
{
<SfGrid DataSource="@Employees">
<GridColumns>
<GridColumn Field=@nameof(Employee.EmployeeId) HeaderText="ID"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field=@nameof(Employee.FirstName) HeaderText="First Name"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field=@nameof(Employee.LastName) HeaderText=" Last Name"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field=@nameof(Employee.Email) HeaderText="Email"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field=@nameof(Employee.DepartmentId) HeaderText="Department"></GridColumn>
</GridColumns>
</SfGrid>
}
@code{
public List<Employee> Employees { get; set; } = null;
[Inject]
public IEmployeeService EmployeeService { get; set; }
protected override async Task OnInitializedAsync()
{
Employees = (await EmployeeService.GetEmployees()).ToList();
}
}SQL Script
SQL Script used in the video to populate test data in Employees table.
Declare @TotalRowsToInsert int = 25
Declare @Counter int = 1
DECLARE @StartDate DATE = '1980-01-01'
DECLARE @EndDate DATE = '2020-12-31'
WHILE(@Counter <= @TotalRowsToInsert)
BEGIN
DECLARE @FirstName NVARCHAR(10) = 'fn' + RTRIM(@Counter)
DECLARE @LastName NVARCHAR(10) = 'ln' + RTRIM(@Counter)
DECLARE @Email NVARCHAR(50) = @FirstName + @LastName + '@pragimtech.com'
-- Select a Random Date
DECLARE @DoB DATETIME = DATEADD(DAY, RAND(CHECKSUM(NEWID()))*(1+DATEDIFF(DAY, @StartDate, @EndDate)), @StartDate)
-- Select a Random Number between 0 and 2
DECLARE @Gender INT = FLOOR(RAND() * 3);
-- Select a Random Number between 1 and 4
DECLARE @DeptId INT = ABS(CHECKSUM(NEWID()) % 4) + 1
INSERT INTO Employees VALUES (@FirstName, @LastName, @Email, @DoB, @Gender, @DeptId, null)
SET @Counter = @Counter + 1
ENDEnable DataGrid Paging in Blazor
- To enable paging, simply set
AllowPaging="true" - Use
PageSizeproperty ofGridPageSettingsto specify the number of rows you want to display on each page. - Use
PageCountproperty to specify the number of pages to display in the pager. - Use
PageSizesproperty to render DropDownList in the pager which allow the user to select page size from the DropDownList.
@if (Employees != null)
{
<SfGrid DataSource="@Employees" AllowPaging="true">
<GridPageSettings PageSize="10" PageCount="5" PageSizes="@pagerDropdown">
</GridPageSettings>
<GridColumns>
<GridColumn Field=@nameof(Employee.EmployeeId) HeaderText="ID"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field=@nameof(Employee.FirstName) HeaderText="First Name"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field=@nameof(Employee.LastName) HeaderText=" Last Name"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field=@nameof(Employee.Email) HeaderText="Email"></GridColumn>
<GridColumn Field=@nameof(Employee.DepartmentId) HeaderText="Department"></GridColumn>
</GridColumns>
</SfGrid>
}
@code{
string[] pagerDropdown = new string[] { "All", "5", "10", "15", "20" };
public List<Employee> Employees { get; set; } = null;
[Inject]
public IEmployeeService EmployeeService { get; set; }
protected override async Task OnInitializedAsync()
{
Employees = (await EmployeeService.GetEmployees()).ToList();
}
}Client-Side and Server-Side Paging
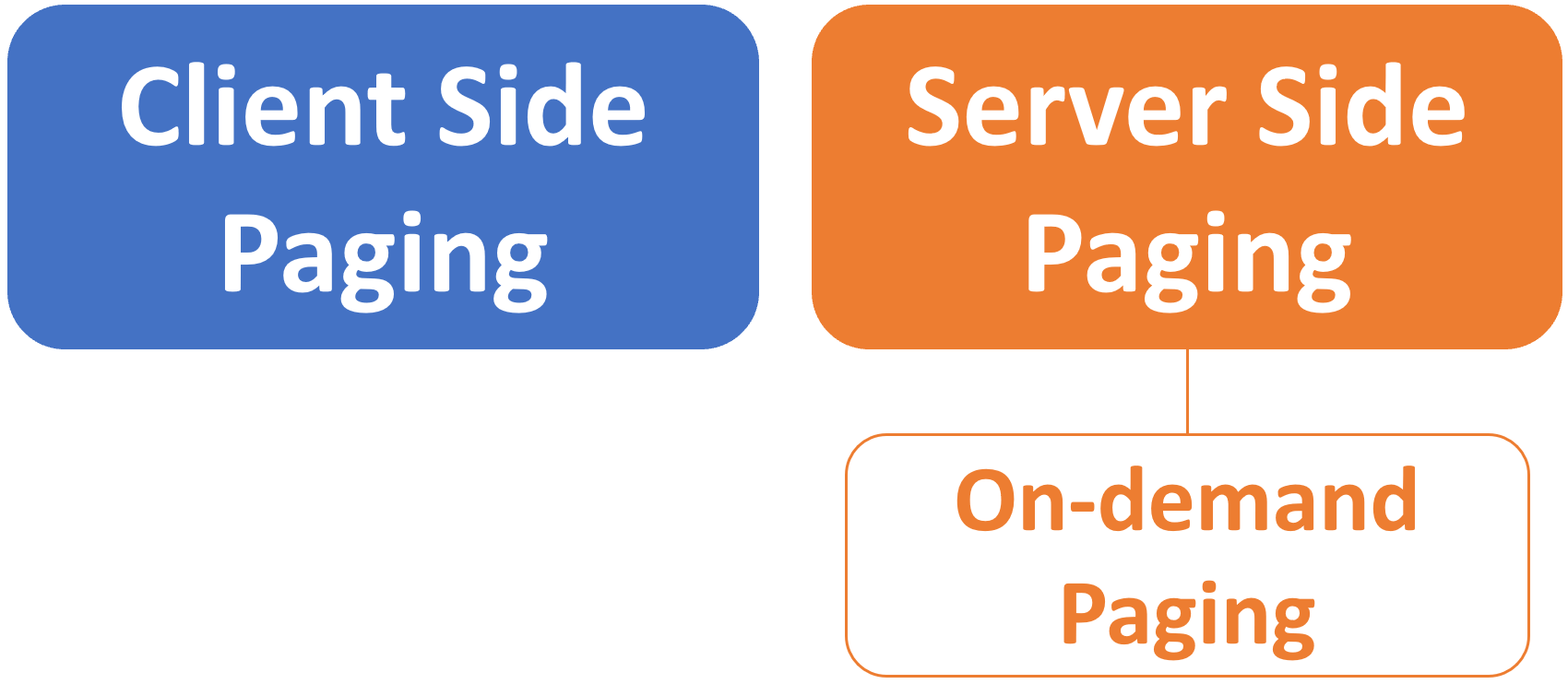
At the moment all the data is retrieved from the server onto the client machine. The paging is performed on the client-side. This is called client-side paging and it works fine if the number of rows are less, may be a few hundered or even a thousand, but if you have millions of rows, server-side paging (also called on-demand paging) provides better performance over client-side paging. We will discuss implementing server-side paging in a later video.
Loggin Entity Framework Core SQL commands
If you want to log the SQL Commands sent to the database, include the following configuration in appsettings.json
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Database.Command": "Information"
}
}© 2020 Pragimtech. All Rights Reserved.

